
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laser Fusion Research Center, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang, Sichuan 621900, People’s Republic of China
2 Institute of Applied Physics and Computational Mathematics, Beijing 100094, People’s Republic of China
In an experiment performed on the Shenguang-III prototype laser facility, collective Thomson scattering (TS) is used to study the spatial growth of stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) in a gas-filled hohlraum by detecting the SBS-driven ion acoustic wave. High-quality time-resolved SBS and TS spectra are obtained simultaneously in the experiment, and these are analyzed by a steady-state code based on the ray-tracing model. The analysis indicates that ion–ion collisions may play an important role in suppressing SBS growth in the Au plasma; as a result, the SBS excited in the filled gas region is dominant. In the early phase of the laser pulse, SBS originates primarily from the high-density plasma at the edges of the interaction beam channel, which is piled up by the heating of the interaction beam. Throughout the duration of the laser pulse, the presence of the TS probe beam might mitigate SBS by perturbing the density distribution around the region overlapping with the interaction beam.
Matter and Radiation at Extremes
2024, 9(2): 027601
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laboratory of Computational Physics, Institute of Applied Physics and Computational Mathematics, Beijing 10088, China
2 Institute of Applied Physics and Computational Mathematics, Beijing 10088, China
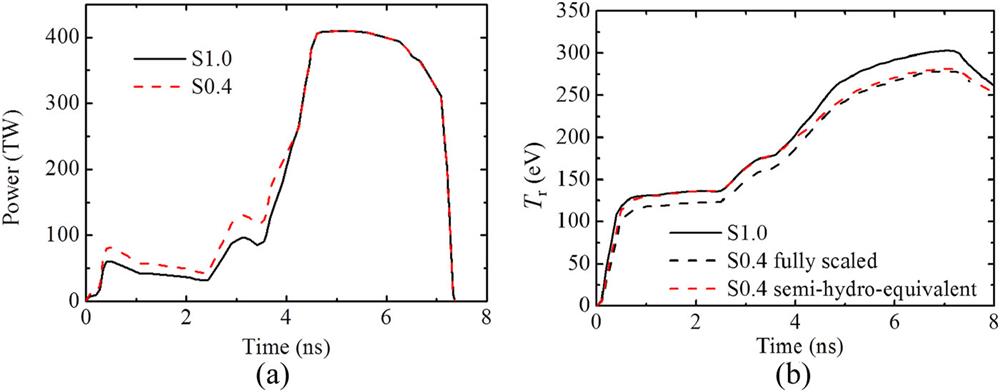
Extrapolation of implosion performance between different laser energy scales is investigated for indirect drive through a semi-hydro-equivalent design. Since radiation transport is non-hydro-equivalent, the peak radiation temperature of the hohlraum and the ablation velocity of the capsule ablator are not scale-invariant when the sizes of the hohlraum and the capsule are scale-varied. A semi-hydro-equivalent design method that keeps the implosion velocity Vi, adiabat αF, and (where PL is the laser power and Rhc is the hohlraum and capsule scale length) scale-invariant, is proposed to create hydrodynamically similar implosions. The semi-hydro-equivalent design and the scaled implosion performance are investigated for the 100 kJ Laser Facility (100 kJ-scale) and the National Ignition Facility (NIF-scale) with about 2 MJ laser energy. It is found that the one-dimensional implosion performance is approximately hydro-equivalent when Vi and αF are kept the same. Owing to the non-hydro-equivalent radiation transport, the yield-over-clean without α-particle heating (YOCnoα) is slightly lower at 100 kJ-scale than at NIF-scale for the same scaled radiation asymmetry or the same initial perturbation of the hydrodynamic instability. The overall scaled two-dimensional implosion performance is slightly lower at 100 kJ-scale. The general Lawson criterion factor scales as (where S is the scale-variation factor) for the semi-hydro-equivalent implosion design with a moderate YOCnoα. Our study indicates that χnoα ≈ 0.379 is the minimum requirement for the 100 kJ-scale implosion to demonstrate the ability to achieve marginal ignition at NIF-scale.
Matter and Radiation at Extremes
2024, 9(1): 015601
1 中国地质大学(武汉)珠宝学院,湖北 武汉 430074
2 中国地质大学(武汉)先进制造研究所,湖北 武汉 430074
3 湖北三江航天江北机械工程有限公司,湖北 孝感 432000
4 中国地质大学(武汉)机械与电子信息学院,湖北 武汉 430074
5 鑫精合激光科技有限公司,北京 102200
铜铬锆(CuCrZr)作为沉淀硬化合金,以其良好的耐热性、耐腐蚀性以及优异的力学、电学和热学性能而被广泛应用于航空航天、核能化工等领域。然而,CuCrZr是当前激光增材制造(LAM)难成形材料之一,相关研究报道还很有限。本文综述了近年来激光粉末床熔融(L-PBF)制备CuCrZr合金的研究进展,重点探究了绿激光与近红外激光对成形质量的影响规律,分析了热处理及构建方向与微观组织、力学性能的内在联系,并研究了热处理对于电学、热学性能的强化机制。近红外激光制备样品的致密度波动范围大(95.5%~99.9%),绿激光制备样品的整体致密度较低但波动范围较小(96.5%~98.5%),工艺参数仍有优化空间。合金的微观组织和综合性能都存在各向异性,即沿水平方向的晶粒细小,沿垂直方向的晶粒为柱状晶粒。固溶处理会使合金的熔池边界消失并改变晶粒形态,时效处理导致合金产生沉淀并改变晶粒取向。500 ℃左右处理1~2 h的直接时效处理对力学性能的提升最大,时效处理通过降低位错密度、减少热残余应力和促进沉淀物的形成,显著增强了合金的力学性能。对电学、热学性能提升最大的热处理条件为950~1000 ℃的固溶退火处理1 h+500 ℃左右的时效硬化处理1~3 h,这是因为固溶退火+时效硬化处理降低了位错密度和残余应力,并产生了有益的沉淀物。本文总结了L-PBF制备CuCrZr合金的成形行为、微观组织和综合性能的研究进展,并对其研究前景和发展方向进行了展望。
激光增材制造 铜铬锆合金 成形行为 微观组织 综合性能
暨南大学光子技术研究院广东省光纤传感与通信技术重点实验室,广东 广州 510632
基于光纤中的瑞利、布里渊、拉曼等散射效应以及弱反射阵列的分布式光纤传感(DOFS)能够对光纤损耗、温度、应变、振动、声音等多种参量实现长距离、高空间分辨率的实时监测,受到了越来越多的关注,具有非常广阔的应用。在DOFS中使用编码脉冲序列增加DOFS的信号能量,是提高传感性能的一个重要技术途径。因此,编码技术的应用一直是DOFS研究的一个重要领域。综述了DOFS中编码技术的研究进展,阐述了编码技术提高传感性能的技术原理,归纳了不同编码方案的设计和实现方法,分析了不同类型DOFS的技术特征及其相应的编码技术应用方法。最后,对DOFS中的编码技术的发展进行了展望。
传感器 分布式光纤传感器 编码技术 光纤瑞利传感器 光纤布里渊传感器 光纤拉曼传感器 光纤弱光栅阵列传感器

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Applied Physics and Computational Mathematics, Beijing 100094, China
2 Laser Fusion Research Center, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang, Sichuan 621900, China
3 HEDPS, Center for Applied Physics and Technology, and College of Engineering, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
The first laser–plasma interaction experiment using lasers of eight beams grouped into one octad has been conducted on the Shenguang Octopus facility. Although each beam intensity is below its individual threshold for stimulated Brillouin backscattering (SBS), collective behaviors are excited to enhance the octad SBS. In particular, when two-color/cone lasers with wavelength separation 0.3 nm are used, the backward SBS reflectivities show novel behavior in which beams of longer wavelength achieve higher SBS gain. This property of SBS can be attributed to the rotation of the wave vectors of common ion acoustic waves due to the competition of detunings between geometrical angle and wavelength separation. This mechanism is confirmed using massively parallel supercomputer simulations with the three-dimensional laser–plasma interaction code LAP3D.
Matter and Radiation at Extremes
2023, 8(5): 055602
受光纤中声学声子10 ns的寿命的影响,传统布里渊光时域分析(BOTDA)传感器往往不能做到1 m以内的空间分辨率。利用差分脉冲对(DPP)技术可以突破该限制,实现更高的空间分辨率。但是传统的DPP技术存在测量时间长、差分信号间同步难度高和信噪比低等问题。本文提出一种基于布里渊增益-损耗效应的编码DPP-BOTDA系统,通过将处于斯托克斯频率和反斯托克斯频率的泵浦脉冲光同步注入光纤,利用散射光的布里渊增益-损耗效应在光路上差分,解决了信号间的同步问题,并且测量时间只需要传统DPP技术的一半。还分析了传感系统中掺铒光纤放大器增益特性对脉冲序列解码结果的影响,对增益不均匀条件下的编码增益进行了理论计算。实验结果表明,该系统可以实现50 cm的空间分辨率,与传统的单脉冲DPP-BOTDA系统相比,信噪比提高了3 dB。
传感器 光纤传感器 布里渊散射 差分脉冲对 光脉冲编码 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(9): 0928005

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Laboratory of Computational Physics, Institute of Applied Physics and Computational Mathematics, Beijing 100094, China
A new mechanism for the generation of high intensity speckles by coupling of overlapping beams is discovered and studied in detail. Using three-dimensional simulations, the coupling of overlapping beams smoothed by phase plates and by polarization smoothing are investigated in the regime relevant to inertial confinement fusion studies. It is found that the intensity distribution of the laser beam spot can be changed by nonuniform spatial phase modulation, and the speckles formed by the phase plate can be split into smaller speckles with higher intensities, which is favorable for the generation of laser plasma instabilities. Stimulated Brillouin scattering is compared in simulations with and without coupling of the overlapping incident beams, and the results confirm the enhancement of stimulated Brillouin scattering due to this mechanism.
Matter and Radiation at Extremes
2023, 8(2): 025903
1 成都信息工程大学资源环境学院, 四川 成都 610225
2 青海省气象科学研究所, 青海 西宁 810001
冬季牧草即枯草的存量是生态补偿计算与畜牧生产科学管理的关键基础, 而对青藏高原枯草关键参数认识的不足, 直接限制了高寒冬季枯草监测研究与应用发展。 PROSAIL是一种光学辐射传输模型, 它可以定量描述植被参数与冠层反射率的关系。 利用最新版本PROSAIL模型, 结合野外实测的枯草光谱及叶面积、 叶绿素等10个性状参数数据, 模拟生成了15 000组潜在的枯草光谱数据序列。 通过冬、 夏实测枯草与绿草样方的反射光谱特征分析, 揭示了枯草在可见光波段与近红外波段与绿草的显著差异性, 描述了青藏高原冬季枯草在400~1 300 nm波段近似线性的独特光谱分布特征。 在此基础上, 提出了以红光与绿光波段差值为依据的鲜/枯草光谱区分方法, 并据此实现了15 000组模拟光谱中枯草光谱的初级与二级筛选, 建立了枯草模拟光谱数据序列集。 该模拟光谱数据序列集与实测光谱在400~2 500 nm全波段明显相关, 所有模拟谱线R2均在0.904~0.994之间, 表明该模型能够很好地模拟高寒冬季枯草的反射率光谱。 进一步采用EFAST方法, 对枯草模拟光谱数据序列进行全局敏感性分析, 识别出棕色素、 类胡萝卜素、 花青素、 叶片结构、 热点5个对枯草光谱变化不敏感的参数, 并在此基础上优化枯草敏感参数阈值区间。 最终, 以99%置信区间为标准、 余弦距离为评价函数, OFAT方式再次运行模型, 界定了枯草敏感的参数阈值: 叶面积指数阈值区间为0.2~0.89、 叶绿素含量为0~1.29 μg·cm-2、 平均叶倾角为11°~90°、 等效水厚度为0.000 1~0.005 cm、 干物质含量为0.008~0.05 g·cm-2。 通过对10个枯草性状参数及其取值区间的率定, 提出了枯草光谱关键参数数值区间参考表, 为提高对高寒冬季枯草性状特征的科学认识及探究遥感反演应用技术方法提供理论依据与基础数据。
枯草 PROSAIL模型 参数阈值 敏感性分析 青藏高原 Withered grass PROSAIL model Threshold estimate Sensitivity analysis Qinghai-Tibet Plateau 光谱学与光谱分析
2022, 42(4): 1144
1 中国地质大学(武汉)珠宝学院,湖北 武汉 430074
2 中国地质大学(武汉)先进制造研究所,湖北 武汉 430074
3 华中科技大学武汉光电国家研究中心,湖北 武汉 430074
金属蒸气、飞溅和熔池是激光选区熔化(SLM)增材制造过程中的重要物理现象,与成形质量关联密切。本文基于高时空分辨原位成像系统,研究了SLM成形过程中金属蒸气与飞溅的相互作用。实验发现:金属蒸气不仅可以间接作用于粉末颗粒,即通过卷吸作用诱导的惰性卷吸气流形成粉末飞溅,还可以直接作用于粉末颗粒,即通过抬升力或反冲力使粉末颗粒进入蒸气羽流或落回粉床。得到了从熔池“液基”出射的熔滴飞溅以及从基板“固基”出射的粉末飞溅的速度阈值。将SLM成形过程中的飞溅作为示踪粒子,原位测量获得了蒸气反冲压。研究蒸气反冲力作用下金属蒸气与飞溅的“气-固”相互作用,为深入理解金属蒸气与熔池的“气-液”相互作用等现象奠定了基础。
激光技术 激光选区熔化 金属蒸气 飞溅 动力学 相互作用 增材制造 中国激光
2022, 49(14): 1402202
强激光与粒子束
2022, 34(6): 062001





